What is Tomography?
The principle advantage of tomography is improved contrast resolution.
Since the introduction of computed tomography (CT) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) wiht their excellent contrast resolution, tomography is less frequently used. Tomography is now applied principally to high contrast procedures, such as imaging calcifed kidney stones.
IMAGE RECEPTOR AND TUBE HEAD OF
A GENERAL PURPOSE X-RAY IMAGING SYSTEM

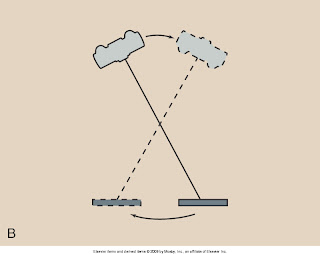
The simpliest tomographic examination is linear tomography. During linear tomography, the xray tube is mechanically attached to the image receptor and moves in one direction, while the image receptor moves in the opposite direction.
The angle of movement is known as the tomographic angle.
- tomographic angle determines the section thickness, or that thickness of tissue will not be blurred.

Relationship of fulcrum, object plane, and tomographic angle
The larger the tomographic angle, the thinner the tomographic section.

Only objects lying in the object plane are properly imaged.
Objects above and below this plane are blurred
because they are imaged across the film.